PTO Driven Hydraulic Pumps for Dump Trucks | Complete Guide
PTO Driven Hydraulic Pumps for Dump Trucks | Complete Guide
If you operate a dump truck, you know that reliable dumping power isn’t just a convenience—it’s a necessity. At the heart of this system lies the Power Take-Off (PTO) driven hydraulic pump, the component that converts your truck’s engine power into the hydraulic force needed to lift that heavy bed. This complete guide will walk you through everything you need to know about PTO driven hydraulic pumps, from how they work and the different types available to how to select the perfect one for your specific truck and job requirements. Understanding this critical component is the first step to maximizing uptime and efficiency on your worksite.
What is a PTO Driven Hydraulic Pump and How Does It Work?
Let’s break down the basics. A PTO driven hydraulic pump is a mechanical device that is bolted directly to a PTO unit on your truck’s transmission or transfer case. The PTO itself is a gearbox that taps into the engine’s rotational power. When you engage the PTO, it drives the pump’s shaft. This pump then draws hydraulic fluid from a reservoir and pressurizes it, sending it to the hydraulic cylinders that raise the dump body.
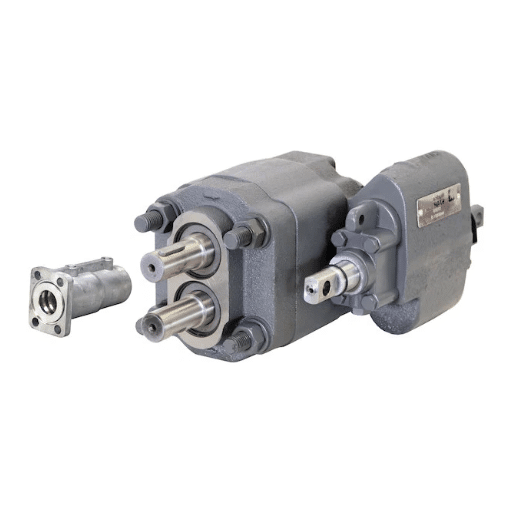
Think of it as a simple but powerful translation of energy: engine power becomes hydraulic power. The key advantage of a PTO pump system is its direct mechanical connection to the engine, which typically provides more consistent and robust power compared to electric alternatives, especially for the high-demand task of lifting a loaded dump bed. This setup is the industry standard for a reason—it’s powerful, efficient, and reliable.
Key Benefits of Using a PTO Pump for Your Dump Truck
Why should you stick with or choose a PTO pump system? The benefits are clear and directly impact your bottom line.
- High Power and Efficiency: By leveraging the truck’s own engine, PTO driven hydraulic pumps deliver immense power, allowing for faster lift times even under full load. This direct drive system is highly efficient, with minimal energy loss.
- Reliability and Durability: These systems are built for tough environments. With fewer electrical components that can fail, a well-maintained PTO pump offers exceptional longevity and dependable performance day in and day out.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Since the power source is already your truck’s engine, you don’t need a separate, dedicated motor. This makes PTO systems a very economical choice for heavy-duty cycling.
- Direct Power Transfer: The mechanical connection provides immediate torque and power, which is crucial for getting a heavy, settled load moving from a complete stop.
Choosing the Right PTO Hydraulic Pump: A Buyer’s Checklist
Not all PTO driven hydraulic pumps are created equal. Selecting the wrong one can lead to poor performance, excessive wear, or even system failure. Here are the critical factors to consider before you buy.
- Pump Type (Gear vs. Piston): This is the most fundamental choice. Gear pumps are common, cost-effective, and robust, perfect for standard dump truck applications. Piston pumps are more complex and expensive but offer higher pressure capabilities and efficiency for specialized, high-demand tasks.
- Flow Rate (GPM) and Pressure (PSI): The flow rate, measured in Gallons Per Minute (GPM), determines how fast the bed will lift. The pressure, measured in Pounds per Square Inch (PSI), determines the lifting force. You must match these specifications to your dump body’s cylinder size and the weight of your typical loads. A pump with insufficient GPM will be slow; one with insufficient PSI won’t be able to lift the load.
- PTO Compatibility: The pump must physically and mechanically match your truck’s specific PTO model. This includes the mounting pattern, shaft size, and rotation direction (clockwise or counter-clockwise).
- Reservoir Capacity: Your hydraulic fluid reservoir must be sized correctly to handle the pump’s flow rate and ensure proper cooling and de-aeration of the fluid.
Gear Pump vs. Piston Pump: Which is Best for Your Dump Truck?
To help you visualize the core differences, here’s a straightforward comparison.
| Feature | Gear Pump | Piston Pump |
|---|---|---|
| Best For | Standard dump truck operations, general hauling | High-pressure applications, extreme-duty cycles |
| Cost | More affordable, lower initial investment | More expensive |
| Efficiency | Good for most tasks, less efficient at high pressures | Higher overall efficiency, especially under high pressure |
| Durability & Lifespan | Very durable, but can wear faster under constant high pressure | Superior longevity in demanding conditions |
| Complexity | Simple design, easier to repair | More complex, requires specialized service |
As noted by a certified fluid power specialist we consulted, “For over 90% of dump truck owners, a quality gear pump is more than sufficient. It provides the perfect balance of power, cost, and reliability. Only consider a piston pump if you’re consistently pushing the limits of your truck’s capacity or operating in extreme cold, where its higher efficiency provides a real advantage.”
Installation Tips and Essential Maintenance Practices
Proper installation and maintenance are non-negotiable for getting the longest life from your PTO driven hydraulic pump.
Installation Pointers: Always ensure the PTO and pump shafts are perfectly aligned to prevent premature wear and vibration. Use the correct grade of hydraulic hose and secure all fittings tightly to prevent leaks. The system must be thoroughly flushed and filled with the clean, manufacturer-recommended hydraulic fluid before initial operation. According to a OSHA report, failures in powered industrial equipment, which include hydraulic systems, are a significant safety concern, making correct installation paramount.
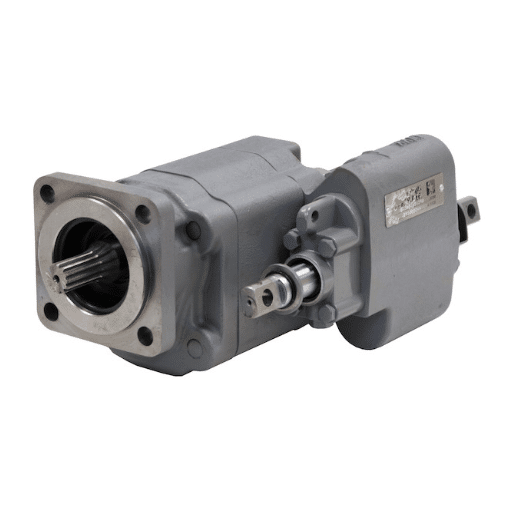
Maintenance Schedule:
- Daily: Check for visible leaks around the pump, hoses, and fittings.
- Weekly/Monthly: Check hydraulic fluid levels and look for signs of contamination or discoloration.
- Annually (or per manufacturer hours): Change the hydraulic fluid and filter. Inspect the pump and PTO for any signs of wear or damage.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: How often should I change the hydraulic fluid in my PTO pump system?
A: A good rule of thumb is to change the fluid and filter every 1,000 operating hours or once a year, whichever comes first. However, always defer to your truck and pump manufacturer’s specific recommendations, as this can vary. If you notice the fluid becoming dark or murky, change it immediately.
Q: My dump truck bed is lifting slowly. Could the PTO pump be the problem?
A: A slow-lifting bed is a classic symptom. While it could be the PTO driven hydraulic pump wearing out, it’s often not the first place to look. First, check for low hydraulic fluid levels, a clogged hydraulic filter, or a worn PTO driveline coupling. If those are in good shape, then the pump’s internal components may be worn and losing efficiency.
Q: Can I install a PTO pump myself, or should I hire a professional?
A: If you have advanced mechanical skills, the right tools, and can ensure perfect alignment, a DIY installation is possible. However, due to the critical nature of the system and the potential for costly errors or safety hazards, it is highly recommended to have a certified technician handle the installation. Data from the National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA) underscores the importance of proper maintenance and installation for all vehicle systems to prevent accidents.
Final Thoughts
Your dump truck’s PTO driven hydraulic pump is a workhorse that deserves your attention. By understanding how it works, choosing the right type for your needs, and committing to a proactive maintenance routine, you can ensure it provides years of reliable service. Investing in the correct PTO hydraulic pump and caring for it properly isn’t just a repair—it’s an investment in the productivity and longevity of your entire operation.
Sources:
- Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA). Commonly Used Statistics. https://www.osha.gov/data/commonstats
- National Highway Traffic Safety Administration (NHTSA). Vehicle Hydraulic Systems. https://www.nhtsa.gov/equipment/hydraulic-systems