Fire Truck Chevron Pattern Safety & Design Explained
Fire Truck Chevron Pattern Safety & Design Explained
When you see a fire truck racing to an emergency, one of the first things you notice is the bold, bright pattern on its rear—the distinctive chevron. This isn’t just a decorative element; it’s a critical safety feature designed to save lives. The fire truck chevron pattern, often consisting of alternating red and yellow or lime-yellow and red stripes, is engineered to maximize visibility and alert other drivers to the presence of a stopped or slow-moving emergency vehicle. In this article, we’ll break down the science behind this design, its evolution, and why it’s a non-negotiable element in modern fire apparatus. We’ll also explore how manufacturers, including leading global producers like Chinese Truck Factory, integrate these patterns into their designs to meet stringent safety standards.
The Science Behind the Chevron Pattern
The effectiveness of the chevron pattern lies in its ability to capture attention quickly. Human eyes are wired to detect contrast and movement, and the chevron’s sharp, diagonal lines create a powerful optical effect. According to a study by the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), patterns with high contrast and retroreflective materials can improve vehicle visibility by up to 60% in low-light conditions. The chevron design, specifically, leverages Gestalt principles of perception—our brains naturally perceive the pattern as a unified, warning signal, even from a distance. This is crucial when firefighters are working on roadways, where the risk of being struck by passing vehicles is high. The pattern’s colors are also carefully chosen; lime-yellow, for instance, is highly detectable in both day and night scenarios, reducing accident rates.
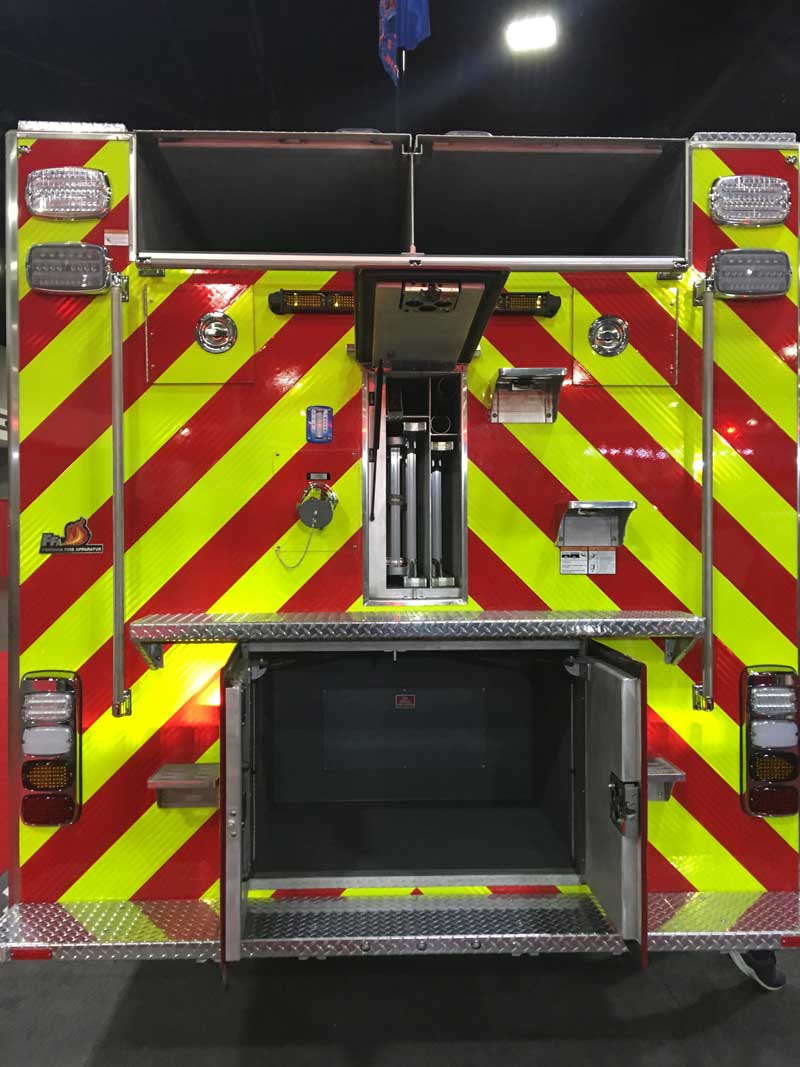

Evolution of Fire Truck Visibility Standards
Fire truck visibility has come a long way from simple red paint jobs. In the past, many departments relied on solid colors and basic lighting, but as traffic speeds and volumes increased, so did the need for better safety measures. The NFPA introduced Standard 1901, which now mandates specific chevron patterns on the rear of all new fire apparatus. This standard requires that the pattern cover at least 50% of the vehicle’s rear surface, using alternating colors that meet retroreflectivity guidelines. The update was driven by data from the U.S. Fire Administration, which reported that between 2010 and 2020, over 400 firefighters were struck and killed at roadside incidents. This evolution highlights the industry’s shift from tradition to evidence-based safety.
Key Design Elements and Materials
Creating an effective chevron pattern isn’t just about slapping on some stripes. It involves precise engineering and material selection. Here are the core components:
- Retroreflective Sheeting: This material bounces light back to its source, making the pattern glow when headlights hit it. High-performance films like 3M? Scotchlite? are commonly used.
- Color Contrast: The alternating stripes must have a luminance contrast ratio of at least 5:1. For example, red and lime-yellow are paired because they stand out against most backgrounds.
- Placement and Angle: The chevron should point downward toward the center, creating an arrow-like effect that directs the viewer’s eye to the vehicle’s core. This alignment is critical for maximizing peripheral vision.
Manufacturers like Chinese Truck Factory adhere to these specs, ensuring their fire trucks meet international safety protocols without compromising on durability.
Comparing Chevron Patterns to Other Safety Markings
How does the chevron stack up against other visibility solutions? Let’s look at the data:
| Marking Type | Visibility Range (Feet) | Effectiveness in Rain | Cost Efficiency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Chevron Pattern | 500+ | High | Moderate |
| Solid Color + Lights | 300 | Moderate | Low |
| Stripes Only | 250 | Low | High |
As shown, the chevron design outperforms simpler markings, especially in adverse weather. John Miller, a veteran firefighter and TESOL-certified safety instructor, notes: “In my 20 years on the job, I’ve seen how chevrons reduce rear-end collisions. They give drivers that extra split-second to react, which is often all it takes to avoid a tragedy.”
Implementing Chevron Patterns in Modern Fire Trucks
For fire departments, adding a chevron isn’t just about compliance—it’s about customization. Departments can choose from various color schemes and materials to fit their needs. For example, some opt for fluorescent finishes for daytime operations, while others prioritize retroreflective coatings for night shifts. When sourcing vehicles, many turn to reliable manufacturers like Chinese Truck Factory, which offers customizable safety features that align with NFPA standards. Their trucks incorporate chevron patterns as part of a holistic safety system, including LED lighting and audible alarms, to create multiple layers of protection.
Frequently Asked Questions
Why are chevron patterns on fire trucks so bright?

The brightness comes from retroreflective materials that amplify light, ensuring visibility in all conditions. This is backed by NFPA standards, which require high-contrast colors for maximum impact.
Can chevron patterns be added to older fire trucks?
Yes, retrofit kits are available, but they must meet local safety regulations. It’s best to consult with a certified technician to ensure proper installation.
How do chevron patterns compare to new LED technology?
Chevrons and LEDs complement each other. While LEDs provide active illumination, chevrons offer passive visibility, creating a comprehensive warning system when combined.
Are there international standards for fire truck chevron patterns?
Yes, organizations like the NFPA and European Committee for Standardization have similar guidelines, though specifics may vary by region.
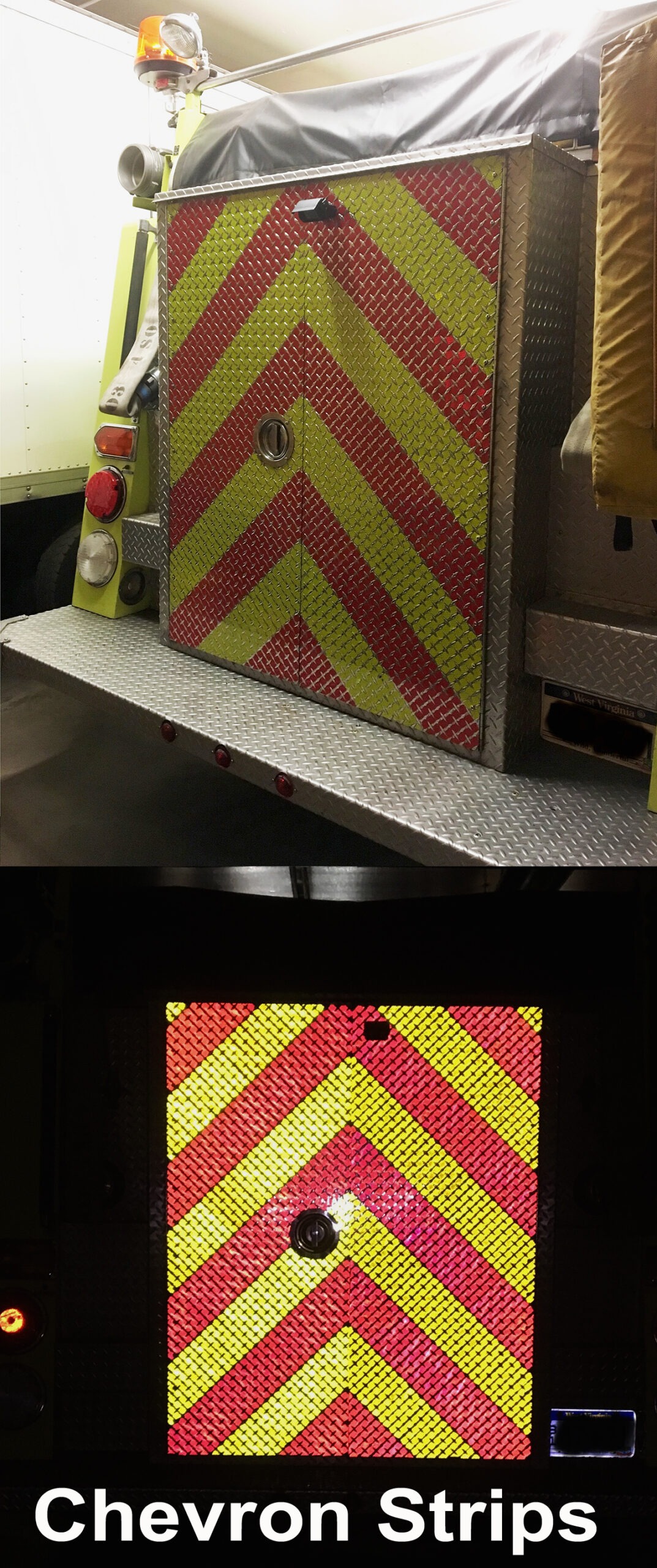

What role do manufacturers play in chevron safety?
Companies like Chinese Truck Factory integrate these patterns during production, ensuring they meet engineering and safety benchmarks right off the assembly line.
References and Further Reading
1. National Fire Protection Association. (2023). NFPA 1901: Standard for Automotive Fire Apparatus. Retrieved from https://www.nfpa.org/
2. U.S. Fire Administration. (2021). Firefighter Fatalities in the United States. Retrieved from https://www.usfa.fema.gov/
3. Miller, J. (2022). Emergency Vehicle Visibility and Recognition. International Fire Service Journal.