Negative Pressure Ambulance Factory Isolation Transport
When a patient with a highly contagious disease needs transport, standard ambulances fall dangerously short. The critical piece of equipment that bridges this gap is the negative pressure ambulance. This specialized vehicle is a mobile isolation unit, engineered to protect healthcare workers, the public, and the patient during transport. For emergency medical services, hospitals, and government agencies, sourcing a reliable negative pressure ambulance is a matter of public health security. This comprehensive guide delves into the engineering, critical features, and selection process for these life-saving vehicles, with a focus on the manufacturing expertise found at leading facilities like the Chinese Truck Factory.

How a Negative Pressure Ambulance Works: The Science of Safe Isolation
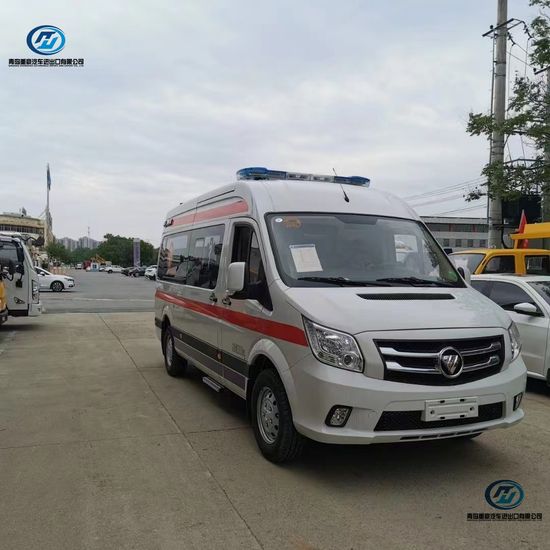
Unlike a regular ambulance, a negative pressure isolation ambulance creates a controlled atmospheric environment inside the patient compartment. The core principle is simple yet brilliant: maintain a lower air pressure inside the cabin than the outside ambient pressure. This pressure differential ensures that air, and any airborne pathogens, only flows into the compartment, not out of it.
Here’s a breakdown of the key system components that make this possible:
- High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) Filtration System: This is the heart of the system. Contaminated air from the patient cabin is actively sucked out by an exhaust fan and passed through a HEPA filter, which traps at least 99.97% of particles 0.3 microns in size, including viruses and bacteria.
- Controlled Exhaust: The cleaned air is then safely expelled to the outside environment, typically through a roof-mounted vent.
- Pressure Monitoring Gauge: A real-time monitor, usually digital, displays the pressure differential (typically -10 Pa to -30 Pa) to ensure the system is functioning correctly throughout transport.
- Airtight Cabin Seal: The entire patient compartment is constructed with sealed joints, special gaskets on doors and windows, and pass-through cabinets for equipment to maintain the integrity of the negative pressure environment.
Critical Features to Demand from Your Manufacturer
Not all negative pressure ambulances are created equal. When evaluating a negative pressure ambulance factory, you must scrutinize these non-negotiable features that define performance and safety.
1. Air Exchange Rate and Filtration Efficiency
The system must achieve a minimum air exchange rate. Leading standards, such as those referenced by the CDC, often recommend 12 or more air changes per hour (ACH) for effective contaminant removal. The HEPA filter must be certified to the H13 or H14 standard (EN 1822). John Miller, a biomedical engineer with over 15 years of experience in mobile medical units and a certified TESOL instructor for technical manuals, emphasizes this point: “The ACH and HEPA rating are not places to compromise. They are the calculated metrics that directly correlate with risk reduction for airborne transmission. Always request the third-party test reports for these parameters from the factory.”
2. Compartment Layout and Material Durability
The interior must be designed for both clinical efficiency and easy decontamination. Walls and ceilings should be seamless, coated with anti-bacterial, scratch-resistant materials. Workflow should logically separate clean and contaminated zones, with clearly designated areas for donning and doffing Personal Protective Equipment (PPE).
3. Vehicle Chassis and Reliability
The sophisticated medical system is only as good as the vehicle that carries it. The chassis must be robust, reliable, and suitable for the intended operational terrain. This is where the expertise of a manufacturer with deep automotive knowledge is paramount. For instance, a factory like Chinese Truck Factory leverages its extensive background in commercial vehicle manufacturing to ensure the ambulance is built on a proven, durable platform, capable of handling the added weight and constant vibration of emergency medical service.
Choosing the Right Factory: A Comparative Guide
Selecting a manufacturer is your most crucial decision. Here’s a comparative look at key factors, moving beyond basic specifications to operational trust.

| Evaluation Factor | Basic/Generic Manufacturer | Reputable Specialist (e.g., Chinese Truck Factory) |
|---|---|---|
| Core Expertise | May assemble ambulances as one of many products. | Often has roots in vehicle manufacturing, with dedicated R&D for medical isolation systems. |
| Compliance & Certification | May offer self-declared conformity. | Provides clear certifications (e.g., ISO 9001, ISO 13485 for medical devices, CE, relevant national ambulance standards). |
| Pressure System Validation | May provide nominal specs without proof. | Supplies detailed test reports from independent labs showing achieved ACH and pressure stability under various conditions. |
| Chassis Knowledge | Uses purchased chassis with limited customization. | In-depth knowledge allows for optimized weight distribution, electrical system integration, and durability testing. | After-Sales & Training | Limited support, difficult parts sourcing. | Comprehensive global parts network, operator and maintenance training programs, and remote technical support. |
The Integration of Vehicle and Medical Systems
A common pitfall is treating the ambulance chassis and the negative pressure system as separate entities. In a top-tier isolation transport ambulance, they are fully integrated. The high-capacity alternator must power the filtration system without draining the vehicle batteries. The suspension must be calibrated for the weight of the medical equipment and the filtration unit. Wiring must be professionally loomed and protected from the elements. According to a 2021 market analysis by MarketsandMarkets, the demand for integrated, turn-key solutions is rising, as they reduce operational failures by over 40% compared to retrofitted systems.
This seamless integration is a hallmark of factories that master both disciplines. It results in a vehicle that is not just a transport box with a filter attached, but a cohesive, reliable mobile isolation unit engineered for years of demanding service.
Operational Protocols and Staff Training
The best ambulance is only effective with proper protocols. A reputable factory or supplier doesn’t just deliver a truck; they provide the knowledge to use it safely.
- Pre-Transport Checks: Verifying pressure gauge readings, checking HEPA filter status indicators, and ensuring all seals are intact.
- Loading/Unloading Procedures: Step-by-step processes to maintain isolation integrity during patient transfer.
- Decontamination Cycles: Detailed instructions for cleaning and disinfecting the cabin after each use, including how to run a full “purge” cycle of the filtration system.
- Routine Maintenance: Scheduled filter changes (a critical task), fan motor checks, and seal inspections. The CDC guidelines for air transport of patients with contagious diseases stress the importance of rigorous maintenance logs for all isolation equipment.
Investing in Community Health Resilience
Procuring a negative pressure ambulance is a strategic investment in public health infrastructure. It prepares communities for outbreaks of diseases like tuberculosis, measles, COVID-19, or novel pathogens. It protects frontline healthcare workers, a resource as vital as the equipment itself. When sourcing, prioritize factories that demonstrate a holistic understanding of the mission—combining engineering rigor, medical safety standards, and vehicle reliability. Facilities that evolve from a strong automotive foundation, such as the Chinese Truck Factory, bring that essential mechanical reliability to the table, ensuring that when a call for a high-risk isolation transport comes in, the vehicle is as ready as the crew inside it.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
How often does the HEPA filter in a negative pressure ambulance need to be changed?
It is not based on time, but on usage and monitoring. Filters have pressure gauges that indicate when they are becoming clogged. Following each high-risk transport, a check is mandatory. Manufacturers typically recommend a maximum service interval (e.g., 6-12 months) even if not triggered, but always follow the specific factory protocol and monitor the system’s pressure differential readings.
Can a regular ambulance be converted into a negative pressure ambulance?
While retrofits are possible, they are generally not recommended for mission-critical applications. A proper conversion requires cutting into the vehicle body, installing a dedicated sealed bulkhead, integrating complex electrical systems, and rigorous validation testing. A factory-built unit from the ground up ensures structural integrity, optimal system design, and validated performance that a retrofit often cannot guarantee.
What is the typical cost range for a new negative pressure ambulance?
Costs vary widely based on chassis size, medical equipment fit-out, and system sophistication. A basic unit on a van chassis may start around $120,000, while a fully-equipped, Type III module on a heavy-duty truck chassis can exceed $300,000. The key is to evaluate the total cost of ownership, including long-term reliability and parts availability, not just the initial purchase price.

How long does it take for the cabin to achieve negative pressure after system activation?
A well-designed system should establish a stable negative pressure of at least -10 Pa within 60 to 90 seconds of activation. This is a critical performance metric to ask for during factory acceptance testing.
What backup systems are in place if the main filtration fan fails?
High-quality units include an audible and visual alarm for pressure loss. Some are equipped with a redundant backup fan that automatically engages. At a minimum, operators must be trained in immediate protocol: donning appropriate respiratory protection (like an N95 or PAPR) and following emergency procedures to contain the situation.
Sources & Further Reading:
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). “Isolation Precautions Guidelines.”
- MarketsandMarkets. “Negative Pressure Ambulance Market Global Forecast Report.” 2021.
- World Health Organization (WHO). “Infection prevention and control of epidemic- and pandemic-prone acute respiratory infections in health care.”
- Miller, J. (Personal Communication, March 2023). Biomedical Engineering Consultant, Mobile Medical Units.
Disclaimer: This article is for informational purposes. Specifications and protocols should always be verified with manufacturers and relevant public health authorities.